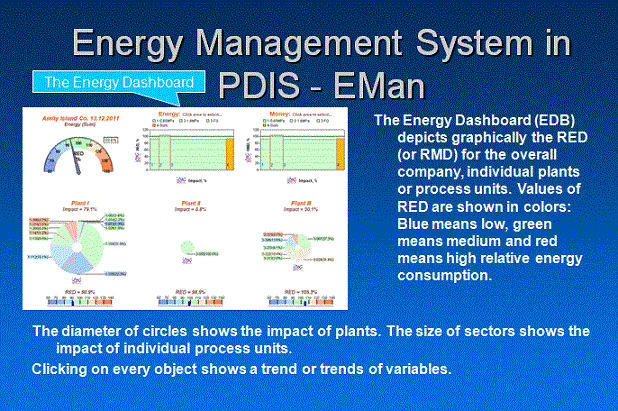
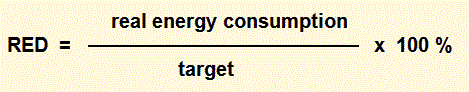Energy Management System
Target
˙Information system for
- Monitoring energy consumption
- Analyzing deviations of energy consumption from a plan (target)
- Root Cause Analysis of deviations
- On-line presenting to users
- Reporting
Prerequisites
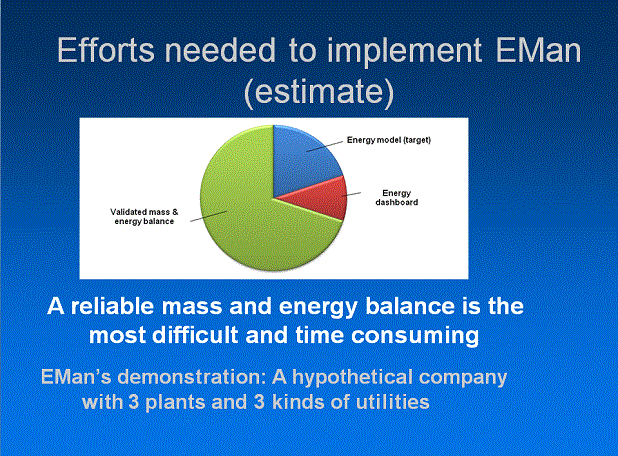
- Consistent (validated) data about
- mass balance (throughputs, yields)
- balance of utilities (energy balance)
- Theoretical target (model) of utilities consumption. Models of increasing complexity
- constant specific consumption (GJ/t of feed, ...)
- influence of Modes of operation, raw material, product quality
- influence of the feed throughput
- ambient temperature
- ...
Models can be created by evaluation of historical data, benchmarking, theoretical analysis, ...
Model should be present in a company+s documentation (Databook, ...).
Important attributes of EMan
- Models (targets) can be dynamic, to reflect changing conditions during production (throughput, ambient temperature, feed quality, modes of operation, ...)
- Results should be based on validated primary data
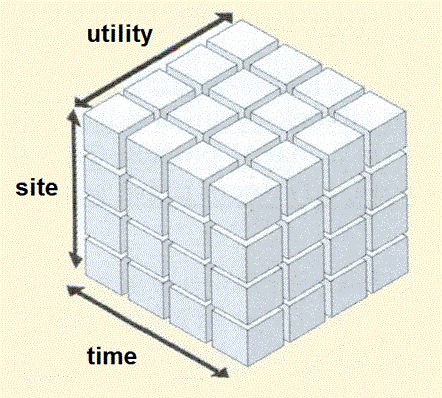
- Respects multidimensionality of the problem, especially the site - utility - time dimensions
- Comparing the real consumption of utilities with a target calculated from a model
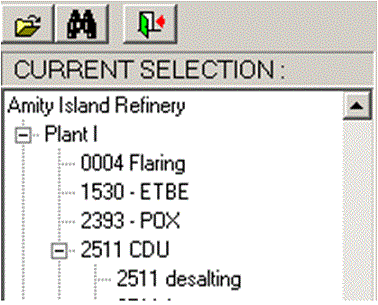
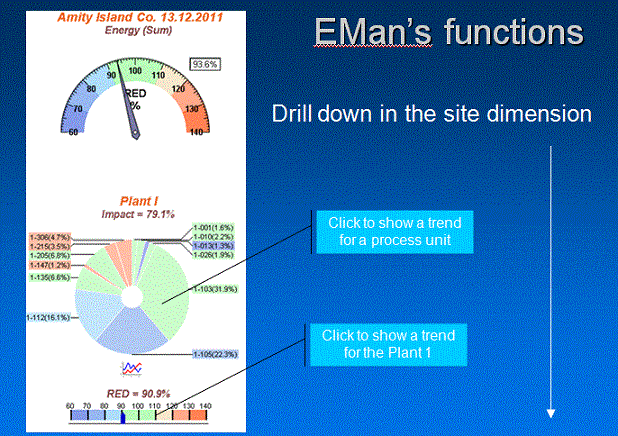
- Structure (hierarchy of the Site dimension Company - Plant - Process Unit)
- Possibility of aggregation in all dimensions
- Trends in the time dimension
- Impact of subsystems on characteristics of the system
- Energy consumption can be expressed in energy or in other units (money, CO2, )
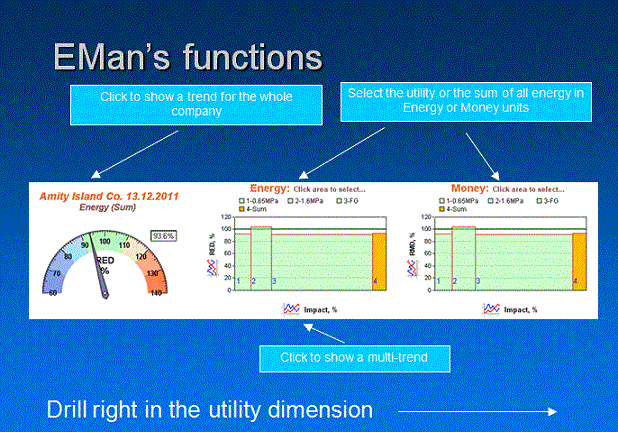
- Application of RCA method (Root Cause Analysis) - the drill down to identify causes of high energy consumption (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Root_cause_analysis).
3 Main dimension of the energy analysis
The Energy OLAP (On/Line Analytical Processing) cube
A tree structure of a company
- Company
- Plant
- Process units
- Equipment
Relative Energy Demand (RED)
The key variable used in energy consumption analysis is RED - Relative Energy Demand
where target is a value calculated from the Company energy model.